You may have noticed a new type of ATM recently appear in your local shopping centre or corner shop, and not thought too much about it. On closer inspection, you would see that it’s a Cryptocurrency ATM, that allows you to deposit cash and get digital assets in return. In fact, there has been a rapid increase in these ATM installations since the beginning of 2023.
Cryptocurrency or ‘crypto’ has been around for more than ten years, but to a lot of people it’s still a mystery. You may have heard about its unpredictability through mainstream media headlines and be familiar with crypto millionaires made famous through social media. It’s hard to avoid stories about cryptocurrency these days, especially given its dramatic rises and falls.
The relatively new asset has interested some investors and sparked caution in others. So, before you decide to use one of these new ATMs or purchase crypto online, you need to know what cryptocurrency is, how it works and whether there are risks involved. Let’s take a closer look.
What is cryptocurrency?
Crypto is a digital form of currency and there are different ‘types’ of cryptocurrencies, just like there are with traditional currencies. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin and Tether are just a few of the different cryptocurrencies available.
Cryptocurrencies use cryptography which means that they’re secured from being counterfeited. If you’re not familiar with cryptography, simply put, it’s a form of encryption and provides a high-level of security. It’s used in bank cards and computing too.
Most cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology which acts like a ledger. Unlike other forms of currency, they’re not reliant on any central bank or financial institution to issue or authorise exchanges. This also means they’re not regulated the same way traditional currencies are.
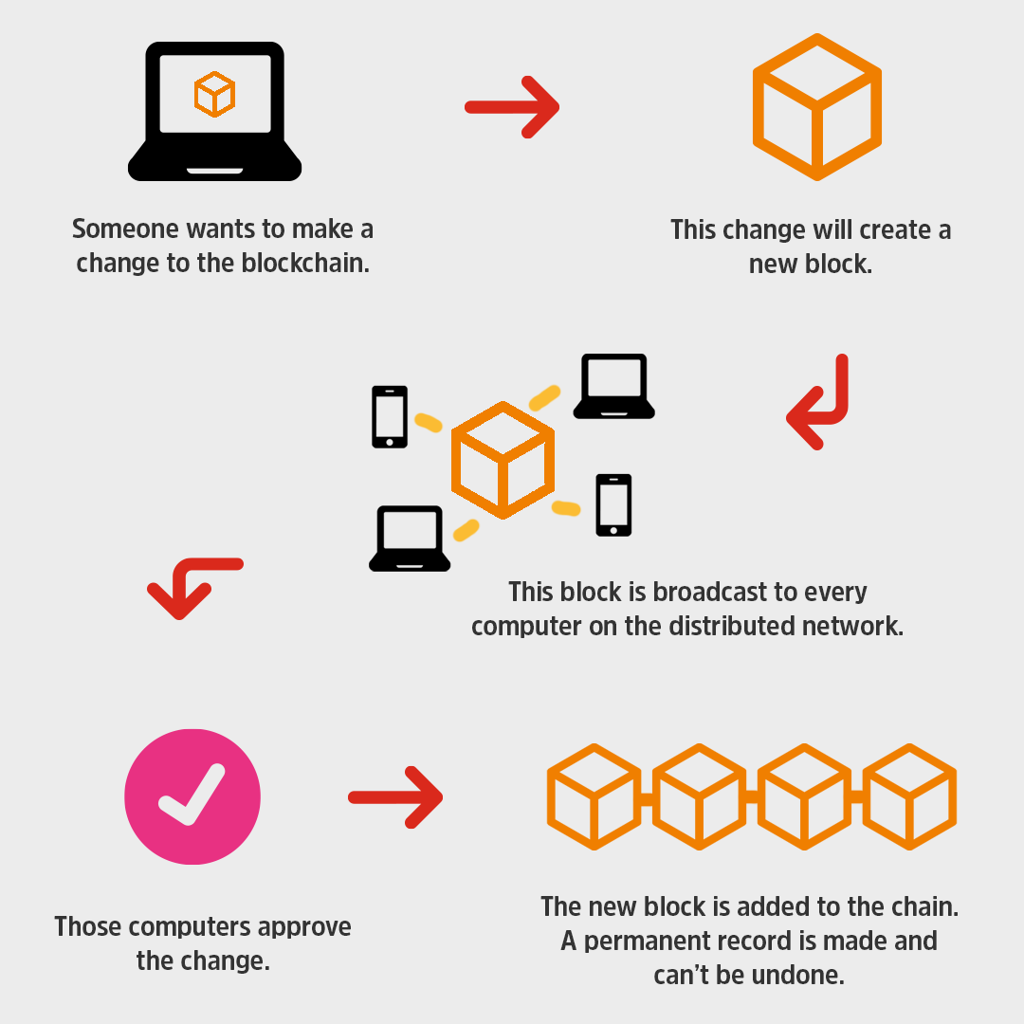
What is blockchain?
A blockchain is a decentralised network of safe and reliable databases that record and distribute transaction information among many computers to validate data, and prevent it from being modified. When it comes to cryptocurrency, the blockchain is a ledger and is used to monitor and record issuances and trades.
How is new cryptocurrency created?
Cryptocurrency is made using a method called ‘mining’, which is when computers are used to solve complex problems. In return for solving the problem, a virtual coin is created – which is the cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin’s programming dictates that no more than 21 million bitcoins can be created, and the coins become exponentially harder to mine every four years. This is part of the reason that the price of Bitcoin has risen so much over the years, and it is the cryptocurrency that most people are likely to have heard of. When it first launched as the first cryptocurrency in 2009, it could be traded for just $0.09!
Is cryptocurrency stored in a bank account?
Crypto is stored in a digital wallet. Like the digital wallet on your phone that you use to store your bank cards so you can tap and go, a crypto digital wallet is protected by a password or ‘key’.
When buying crypto via an online exchange, all the wallet setup and security is managed by the chosen exchange – but there are some stories well circulated online of people forgetting their key and losing access to a ‘fortune’. In some cases, hackers have been able to get into a person’s digital wallet and empty the contents.
Where can cryptocurrency be used?
While cryptocurrency isn’t legal tender in Australia, some vendors here do allow its use for the purchase of goods and services. These include luxury stores and some car retailers, but it’s highly unlikely a cryptocurrency will replace traditional currency any time soon.
A crypto transaction, specifically Bitcoin, costs around US$2.50 to make and takes about ten minutes to complete. Both the cost and time, mean it’s much more complex to use than cash or traditional card payment networks.
What do cryptocurrency scams look like?
Cryptocurrency is often used for illegal activity and investment scams. This is because they’re hard to track and if you lose money to a crypto scam, it’s very unlikely you’ll ever see your money again.
There are plenty of crypto related scams in circulation, and according to Moneysmart, there are three main types. These are:
- investing in a fake crypto exchange, website or app
- fake crypto products or jobs trading crypto
- using crypto to pay scammers.
Each year, investment scams are the type of scam that Australian’s lose the most money to. To learn more about how to spot crypto scams, visit the Moneysmart website.
Crypto is a very high risk and volatile investment. The value can go up or down quickly and there are no guaranteed returns. Before investing in cryptocurrency, it’s important to do your own research, seek guidance from a financial advisor and ensure you fully understand the risks involved.
Sources: Customer Owned Banking Association, The Sydney Morning Herald, Scamwatch, Moneysmart, Investopedia, JetLearn and Insider.
